前面两篇分别介绍了AOP的基本使用姿势和一些高级特性,当时还遗留了一个问题没有说明,即不同的advice,拦截同一个目标方法时,优先级是怎样的,本篇博文将进行详细分析
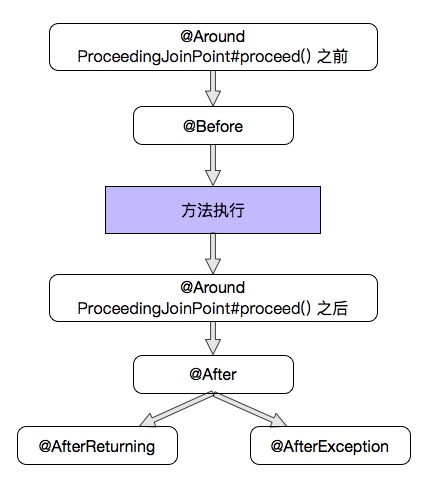
同一个切面中,不同类型的advice的优先级
同一个切面中,同一种类型的advice优先级
不同切面中,同一类型的advice优先级
不同切面中,不同类型的advice优先级
I. 统一切面,不同类型ddvice优先级 在不分析源码的前提下,也只能通过实际的case来看优先级问题了,我们现在设计一下使用实例,通过输出结果来看对应的优先级
1. case设计 首先创建被拦截的bean: com.git.hui.boot.aop.order.InnerDemoBean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Component public class InnerDemoBean public String print () try { System.out.println("in innerDemoBean start!" ); String rans = System.currentTimeMillis() + "|" + UUID.randomUUID(); System.out.println(rans); return rans; } finally { System.out.println("in innerDemoBean over!" ); } } }
接下来写一个切面,里面定义我们常见的各种advice
对于aop的使用,有疑问的可以参考: 190301-SpringBoot基础篇AOP之基本使用姿势小结
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @Component @Aspect public class OrderAspect @Pointcut ("execution(public * com.git.hui.boot.aop.order.*.*())" ) public void point () } @Before (value = "point()" ) public void doBefore (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("do before!" ); } @After (value = "point()" ) public void doAfter (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("do after!" ); } @AfterReturning (value = "point()" , returning = "ans" ) public void doAfterReturning (JoinPoint joinPoint, String ans) System.out.println("do after return: " + ans); } @Around ("point()" ) public Object doAround (ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable try { System.out.println("do in around before" ); return joinPoint.proceed(); } finally { System.out.println("do in around over!" ); } } }
2. 测试 使用SpringBoot的项目进行测试aop,使用还是比较简单的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @SpringBootApplication public class Application private InnerDemoBean innerDemoBean; public Application (InnerDemoBean innerDemoBean) this .innerDemoBean = innerDemoBean; this .innerDemoBean(); } private void innerDemoBean () System.out.println("result: " + innerDemoBean.print()); } public static void main (String[] args) SpringApplication.run(Application.class); } }
看下上面执行的输出结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 do in around before do before! in innerDemoBean start! 1552219604035|e9a31f44-6a31-4485-806a-834361842ce1 in innerDemoBean over! do in around over! do after! do after return: 1552219604035|e9a31f44-6a31-4485-806a-834361842ce1 result: 1552219604035|e9a31f44-6a31-4485-806a-834361842ce1
从输出结果进行反推,我们可以知道统一切面中,advice执行的先后顺序如下
II. 同一切面,同一类型切面 正常来讲,拦截一个方法时,统一类型的切面逻辑都会写在一起,那这个case有什么分析的必要呢?
在我们实际的使用中,同一类型的advice拦截同一个方法的可能性还是很高的,why? 因为多个advice有自己定义的拦截规则,它们之间并不相同,但可能存在交集,比如我们在上面的切面中,再加一个拦截注解的before advice
1. case设计 依然是上面的InnerDemoBean,方法上加一个自定义注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @AnoDot public String print () try { System.out.println("in innerDemoBean start!" ); String rans = System.currentTimeMillis() + "|" + UUID.randomUUID(); System.out.println(rans); return rans; } finally { System.out.println("in innerDemoBean over!" ); } }
然后加一个拦截注解的advice
1 2 3 4 @Before ("@annotation(AnoDot)" )public void doAnoBefore (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("dp AnoBefore" ); }
2. 测试 再次执行前面的case,然后看下输出结果如下
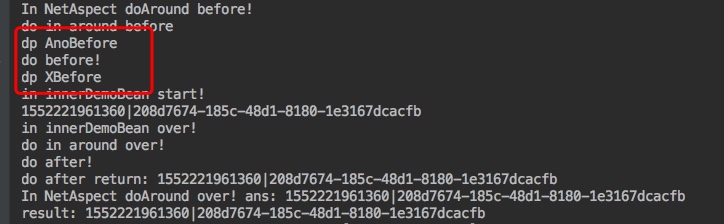
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 In NetAspect doAround before! do in around before dp AnoBefore do before! in innerDemoBean start! 1552221765322|d92b6d37-0025-43c0-adcc-c4aa7ba639e0 in innerDemoBean over! do in around over! do after! do after return: 1552221765322|d92b6d37-0025-43c0-adcc-c4aa7ba639e0 In NetAspect doAround over! ans: 1552221765322|d92b6d37-0025-43c0-adcc-c4aa7ba639e0 result: 1552221765322|d92b6d37-0025-43c0-adcc-c4aa7ba639e0
我们主要看下两个before,发现 AnoBefore 在前面; 因此这里的一个猜测,顺序就是根据方法命名的顺序来的,比如我们再加一个 doXBefore,然后我们预估输出结果应该是
1 do AnoBefore > doBefore > doXBefore
额外添加一个
1 2 3 4 @Before ("@annotation(AnoDot)" )public void doXBefore (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("dp XBefore" ); }
接着就是输出结果如下,和我们预期一致
3. Order注解尝试 我们知道有个Order注解可以来定义一些优先级,那么把这个注解放在advice方法上,有效么?实际尝试一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Order (1 )@Before (value = "point()" )public void doBefore (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("do before!" ); } @Order (2 )@Before ("@annotation(AnoDot)" )public void doAnoBefore (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("dp AnoBefore" ); } @Order (3 )@Before ("@annotation(AnoDot)" )public void doXBefore (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("dp XBefore" ); }
如果注解有效,我们预期输出结果如下
1 do Before > do AnoBefore > do XBefore
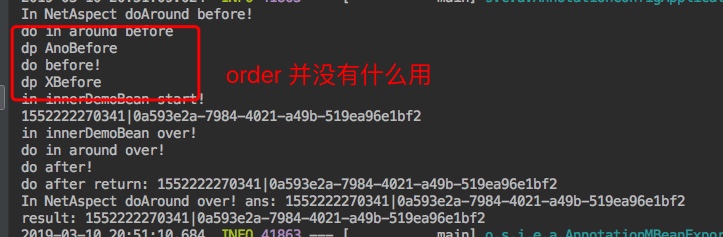
然后再次执行,看下输出结果是否和我们预期一样
4. 小结 同一个切面中,相同的类型的advice,优先级是根据方法命名来的,加@Order注解是没有什么鸟用的,目前也没有搜索到可以调整优先级的方式
III. 不同切面,相同类型的advice 如果说上面这种case不太好理解为啥会出现的话,那么这个可能就容易理解多了;毕竟一个切面完成一件事情,出现相同的advice就比较常见了;
比如spring mvc中,我们通常会实现的几个切面
一个before advice的切面,实现输出请求日志
一个before advice的切面,实现安全校验(这种其实更常见的是放在filter/intercept中)
1. case设计 现在就需要再加一个切面,依然以before advice作为case
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Aspect @Component public class AnotherOrderAspect @Before ("@annotation(AnoDot)" ) public void doBefore () System.out.println("in AnotherOrderAspect before!" ); } }
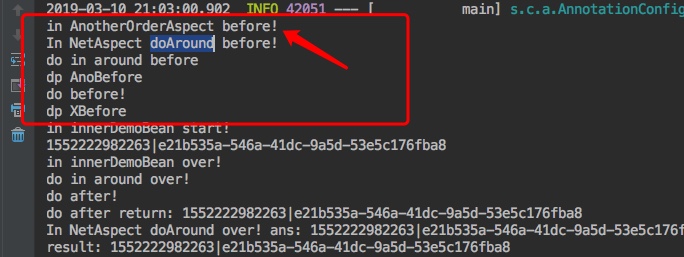
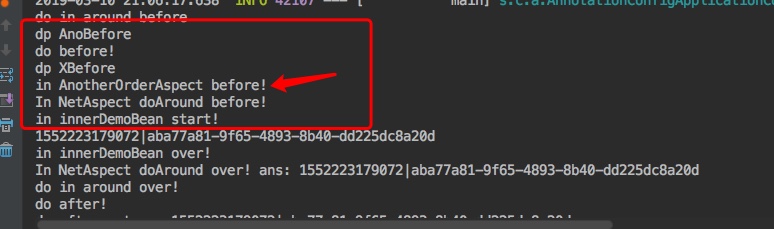
2. 测试 接下来看测试输出结果如下图
发现了一个有意思的事情了,AnotherOrderAspect切面的输出,完全在OrderAspect切面中所有的advice之前,接着我们再次尝试使用@Order注解来试试,看下会怎样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Order (0 )@Component @Aspect public class OrderAspect } @Aspect @Order (10 )@Component public class AnotherOrderAspect }
如果顺序有关,我们预期的输出结果应该是
1 do AnoBefore > do Before > doXBefore > do AnotherOrderAspect before!
实际测试输出如下,和我们预期一致
3. 小结 从上面的测试来看,不同的切面,默认顺序实际上是根据切面的命令来的;
A切面中的advice会优先B切面中同类型的advice
我们可以通过 Order 注解来解决不同切面的优先级问题,依然是值越小,优先级越高
IV. 不同切面,不同advice顺序 其实前面的case已经可以说明这个问题了,现在稍稍丰富一下AnotherOrderAspect,看下结果
1. case设计 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 @Aspect @Order (10 )@Component public class AnotherOrderAspect @Before ("@annotation(AnoDot)" ) public void doBefore () System.out.println("in AnotherOrderAspect before!" ); } @After ("@annotation(AnoDot)" ) public void doAfter (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("do AnotherOrderAspect after!" ); } @AfterReturning (value = "@annotation(AnoDot)" , returning = "ans" ) public void doAfterReturning (JoinPoint joinPoint, String ans) System.out.println("do AnotherOrderAspect after return: " + ans); } @Around ("@annotation(AnoDot)" ) public Object doAround (ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable try { System.out.println("do AnotherOrderAspect in around before" ); return joinPoint.proceed(); } finally { System.out.println("do AnotherOrderAspect in around over!" ); } } }
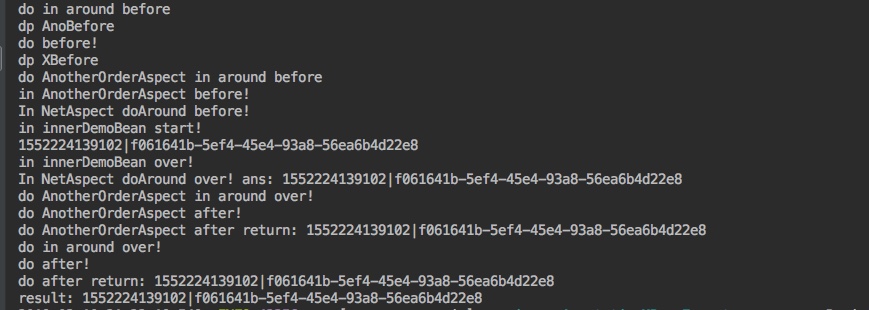
2. 测试 看下执行后的输出结果
假设A切面优先级高于B切面,那么我们执行先后顺序如下
V. 小结 本篇内容有点多,针对前面的测试以及结果分析,给出一个小结,方便直接获取最终的答案
1. 不同advice之间的优先级顺序 1 around 方法执行前代码 > before > 方法执行 > around方法执行后代码 > after > afterReturning/@AfterThrowing
2. 统一切面中相同advice 统一切面中,同类型的advice的优先级根据方法名决定,暂未找到可以控制优先级的使用方式
3. 不同切面优先级 不同切面优先级,推荐使用 @Order注解来指定,数字越低,优先级越高
4. 不同切面advice执行顺序 优先级高的切面中的advice执行顺序会呈现包围优先级低的advice的情况,更直观的先后顺序,推荐看第四节的顺序图,更加清晰明了
VI. 其他 0. 项目
1. 一灰灰Blog
一灰灰的个人博客,记录所有学习和工作中的博文,欢迎大家前去逛逛
2. 声明 尽信书则不如,以上内容,纯属一家之言,因个人能力有限,难免有疏漏和错误之处,如发现bug或者有更好的建议,欢迎批评指正,不吝感激
3. 扫描关注 一灰灰blog
知识星球
打赏
如果觉得我的文章对您有帮助,请随意打赏。
微信打赏
支付宝打赏